Installation¶
Proxmox Backup is split into a server and client part. The server part can either be installed with a graphical installer or on top of Debian from the provided package repository.
System Requirements¶
We recommend using high quality server hardware when running Proxmox Backup in production. To further decrease the impact of a failed host, you can set up periodic, efficient, incremental datastore synchronization from other Proxmox Backup Server instances.
Minimum Server Requirements, for Evaluation¶
These minimum requirements are for evaluation purposes only and should not be used in production.
CPU: 64bit (x86-64 or AMD64), 2+ Cores
Memory (RAM): 2 GB RAM
Hard drive: more than 8GB of space.
Network card (NIC)
Recommended Server System Requirements¶
CPU: Modern AMD or Intel 64-bit based CPU, with at least 4 cores
Memory: minimum 4 GiB for the OS, filesystem cache and Proxmox Backup Server daemons. Add at least another GiB per TiB storage space.
OS storage:
32 GiB, or more, free storage space
Use a hardware RAID with battery protected write cache (BBU) or a redundant ZFS setup (ZFS is not compatible with a hardware RAID controller).
Backup storage:
Prefer fast storage that delivers high IOPS for random IO workloads; use only enterprise SSDs for best results.
If HDDs are used: Using a metadata cache is highly recommended, for example, add a ZFS special device mirror.
Redundant Multi-GBit/s network interface cards (NICs)
Supported Web Browsers for Accessing the Web Interface¶
To access the server's web-based user interface, we recommend using one of the following browsers:
Firefox, a release from the current year, or the latest Extended Support Release
Chrome, a release from the current year
Microsoft's currently supported version of Edge
Safari, a release from the current year
Installation Medium¶
Proxmox Backup Server can be installed via different methods. The recommended method is the usage of an installation medium, to simply boot the interactive installer.
Prepare Installation Medium¶
Download the installer ISO image from https://www.proxmox.com/downloads.
The Proxmox Backup Server installation medium is a hybrid ISO image. It works in two ways:
An ISO image file ready to burn to a DVD.
A raw sector (IMG) image file ready to copy to a USB flash drive (USB stick).
Using a USB flash drive to install Proxmox Backup Server is the recommended way since it is the faster and more frequently available option these days.
Prepare a USB Flash Drive as Installation Medium¶
The flash drive needs to have at least 2 GB of storage space.
Note
Do not use UNetbootin. It does not work with the Proxmox Backup Server installation image.
Important
Existing data on the USB flash drive will be overwritten. Therefore, make sure that it does not contain any still needed data and unmount it afterwards again before proceeding.
Instructions for GNU/Linux¶
On Unix-like operating systems use the dd command to copy the ISO
image to the USB flash drive. First find the correct device name of the
USB flash drive (see below). Then run the dd command. Depending on
your environment, you will need to have root privileges to execute
dd.
# dd bs=1M conv=fdatasync if=./proxmox-backup-server_*.iso of=/dev/XYZ
Note
Be sure to replace /dev/XYZ with the correct device name and adapt
the input filename (if) path.
Caution
Be very careful, and do not overwrite the wrong disk!
Find the Correct USB Device Name¶
There are two ways to find out the name of the USB flash drive. The
first one is to compare the last lines of the dmesg command output
before and after plugging in the flash drive. The second way is to
compare the output of the lsblk command. Open a terminal and run:
# lsblk
Then plug in your USB flash drive and run the command again:
# lsblk
A new device will appear. This is the one you want to use. To be on the extra safe side check if the reported size matches your USB flash drive.
Instructions for macOS¶
Open the terminal (query Terminal in Spotlight).
Convert the .iso file to .dmg format using the convert option of
hdiutil, for example:
# hdiutil convert proxmox-backup-server_*.iso -format UDRW -o proxmox-backup-server_*.dmg
Note
macOS tends to automatically add .dmg to the output file name.
To get the current list of devices run the command:
# diskutil list
Now insert the USB flash drive and run this command again to determine
which device node has been assigned to it. (e.g., /dev/diskX).
# diskutil list
# diskutil unmountDisk /dev/diskX
Note
replace X with the disk number from the last command.
# sudo dd if=proxmox-backup-server_*.dmg bs=1M of=/dev/rdiskX
Note
rdiskX, instead of diskX, in the last command is intended. It will increase the write speed.
Instructions for Windows¶
Using Etcher¶
Etcher works out of the box. Download Etcher from https://etcher.io. It will guide you through the process of selecting the ISO and your USB flash drive.
Using Rufus¶
Rufus is a more lightweight alternative, but you need to use the DD mode to make it work. Download Rufus from https://rufus.ie/. Either install it or use the portable version. Select the destination drive and the downloaded Proxmox ISO file.
Important
Once you click Start, you have to click No on the dialog asking to download a different version of Grub. In the next dialog select DD mode.
Use the Installation Medium¶
Insert the created USB flash drive (or DVD) into your server. Continue by reading the installer chapter, which also describes possible boot issues.
Server Installation¶
The backup server stores the actual backed up data and provides a web based GUI for various management tasks such as disk management.
Note
You always need a backup server. It is not possible to use Proxmox Backup without the server part.
Using our provided disk image (ISO file) is the recommended installation method, as it includes a convenient installer, a complete Debian system as well as all necessary packages for the Proxmox Backup Server.
Once you have created an Installation Medium, the booted installer will guide you through the setup process. It will help you to partition your disks, apply basic settings such as the language, time zone and network configuration, and finally install all required packages within minutes.
As an alternative to the interactive installer, advanced users may wish to install Proxmox Backup Server unattended.
With sufficient Debian knowledge, you can also install Proxmox Backup Server on top of Debian yourself.
While not recommended, Proxmox Backup Server could also be installed on Proxmox VE.
Install Proxmox Backup Server using the Installer¶
Download the ISO from https://www.proxmox.com/downloads. It includes the following:
The Proxmox Backup Server installer, which partitions the local disk(s) with ext4, xfs or ZFS, and installs the operating system
Complete operating system (Debian Linux, 64-bit)
Proxmox Linux kernel with ZFS support
Complete toolset to administer backups and all necessary resources
Web-based management interface
Note
Any existing data on the selected drives will be overwritten during the installation process. The installer does not add boot menu entries for other operating systems.
Please insert the Installation Medium (for example, USB flash drive or DVD) and boot from it.
Note
You may need to go into your server's firmware settings, to enable booting from your installation medium (for example, USB) and set the desired boot order. When booting an installer prior to Proxmox Backup Server version 3.1, Secure Boot needs to be disabled.

After choosing the correct entry (for example, Boot from USB) the Proxmox Backup Server menu will be displayed, and one of the following options can be selected:
Install Proxmox Backup Server (Graphical)
Starts the normal installation.
TIP: It's possible to use the installation wizard with a keyboard only. Buttons
can be clicked by pressing the ALT key combined with the underlined character
from the respective button. For example, ALT + N to press a Next button.
Install Proxmox Backup Server (Console)
Starts the terminal-mode installation wizard. It provides the same overall installation experience as the graphical installer, but has generally better compatibility with very old and very new hardware.
Install Proxmox Backup Server (Terminal UI, Serial Console)
Starts the terminal-mode installation wizard, additionally setting up the Linux kernel to use the (first) serial port of the machine for in- and output. This can be used if the machine is completely headless and only has a serial console available.
Both modes use the same code base for the actual installation process to benefit from more than a decade of bug fixes and ensure feature parity.
TIP: The Console or Terminal UI option can be used in case the graphical installer does not work correctly, due to e.g. driver issues. See also Adding the nomodeset Kernel Parameter.
Advanced Options: Install Proxmox Backup Server (Debug Mode)
Starts the installation in debug mode. A console will be opened at several
installation steps. This helps to debug the situation if something goes wrong.
To exit a debug console, press CTRL-D. This option can be used to boot a
live system with all basic tools available. You can use it, for example, to
repair a degraded ZFS rpool or fix the Host Bootloader for an
existing Proxmox Backup Server setup.
Advanced Options: Install Proxmox Backup Server (Terminal UI, Debug Mode)
Same as the graphical debug mode, but preparing the system to run the terminal-based installer instead.
Advanced Options: Install Proxmox Backup Server (Serial Console Debug Mode)
Same the terminal-based debug mode, but additionally sets up the Linux kernel to use the (first) serial port of the machine for in- and output.
Advanced Options: Rescue Boot
With this option you can boot an existing installation. It searches all attached
hard disks. If it finds an existing installation, it boots directly into that
disk using the Linux kernel from the ISO. This can be useful if there are
problems with the bootloader (GRUB/systemd-boot) or the BIOS/UEFI is unable
to read the boot block from the disk.
Advanced Options: Test Memory (memtest86+)
Runs memtest86+. This is useful to check if the memory is functional and free of errors. Secure Boot must be turned off in the UEFI firmware setup utility to run this option.
You normally select Install Proxmox Backup Server (Graphical) to start the installation.
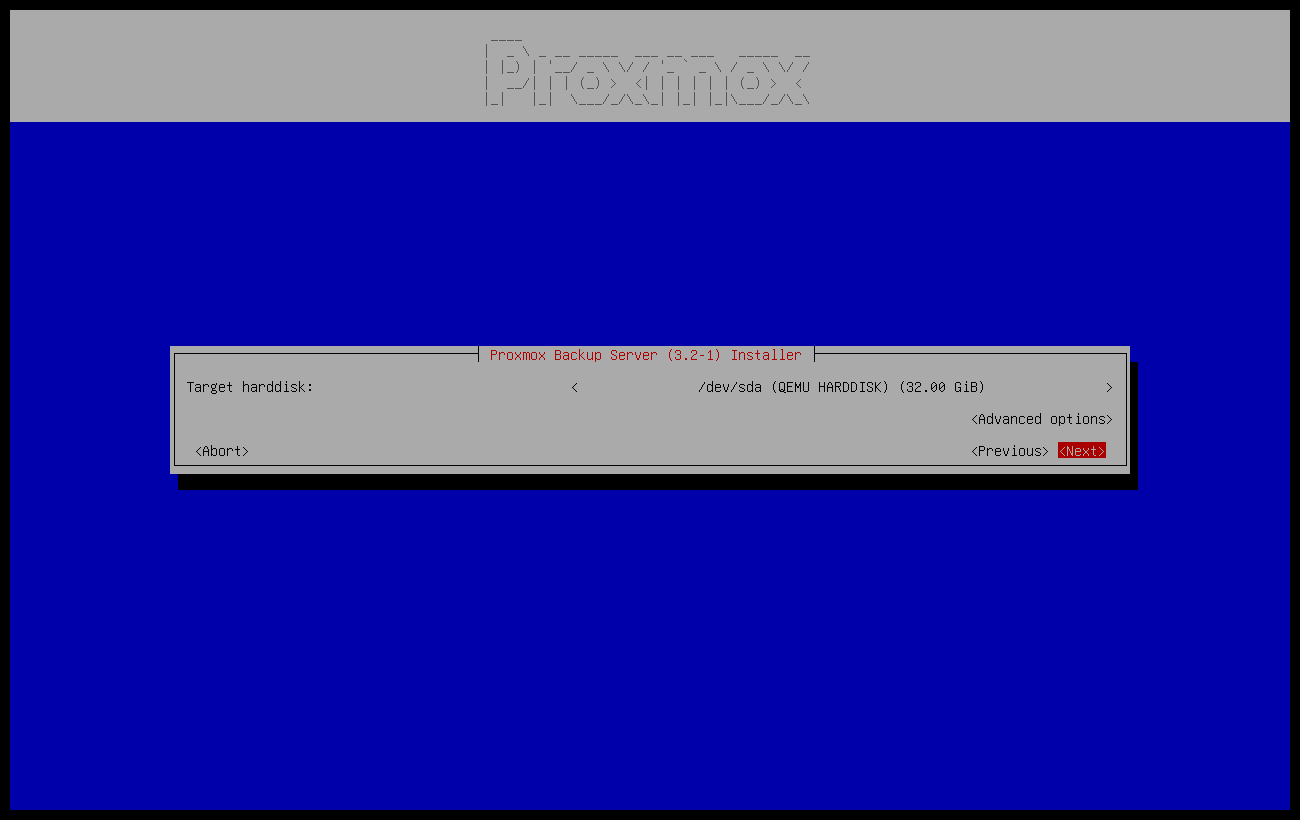
The first step is to read our EULA (End User License Agreement). Following this, you can select the target hard disk(s) for the installation.
Caution
By default, the whole server is used and all existing data is removed. Make sure there is no important data on the server before proceeding with the installation.
The Options button lets you select the target file system, which defaults to
ext4. The installer uses LVM if you select ext4 or xfs as a file
system, and offers additional options to restrict LVM space (see below).
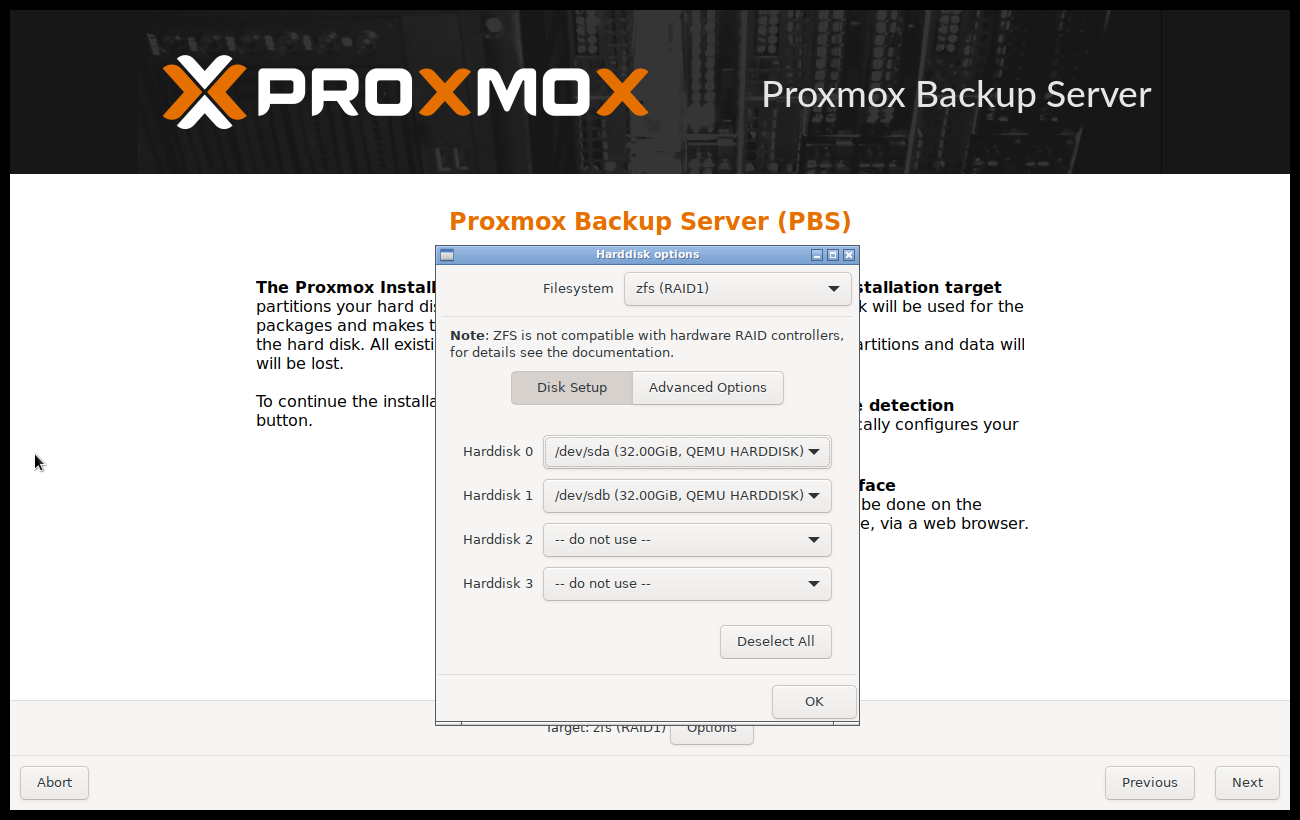
Proxmox Backup Server can also be installed on ZFS. As ZFS offers several software RAID levels, this is an option for systems that don't have a hardware RAID controller. The target disks must be selected in the Options dialog. More ZFS specific settings can be changed under Advanced Options.
Warning
ZFS on top of any hardware RAID is not supported and can result in data loss.
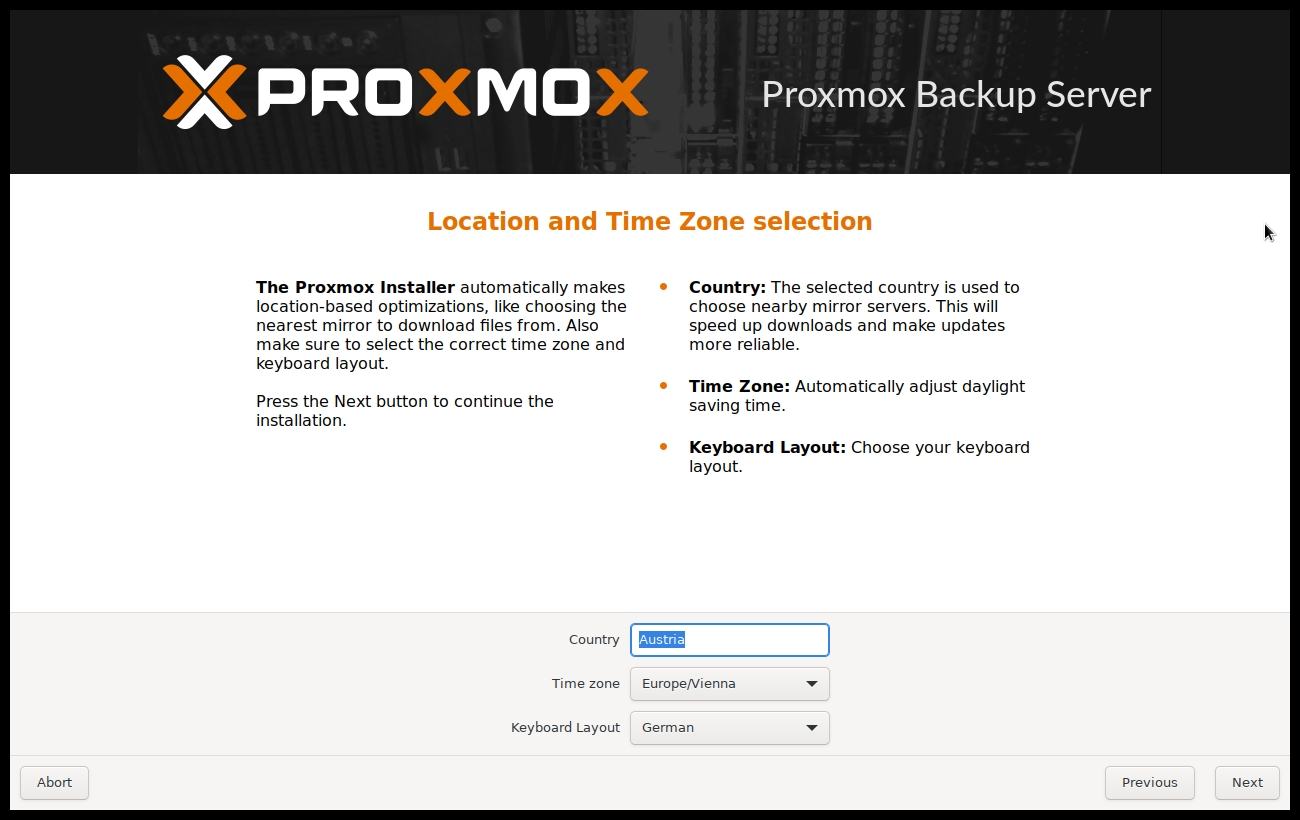
The next page asks for basic configuration options like your location, time zone, and keyboard layout. The location is used to select a nearby download server, in order to increase the speed of updates. The installer is usually able to auto-detect these settings, so you only need to change them in rare situations when auto-detection fails, or when you want to use a keyboard layout not commonly used in your country.
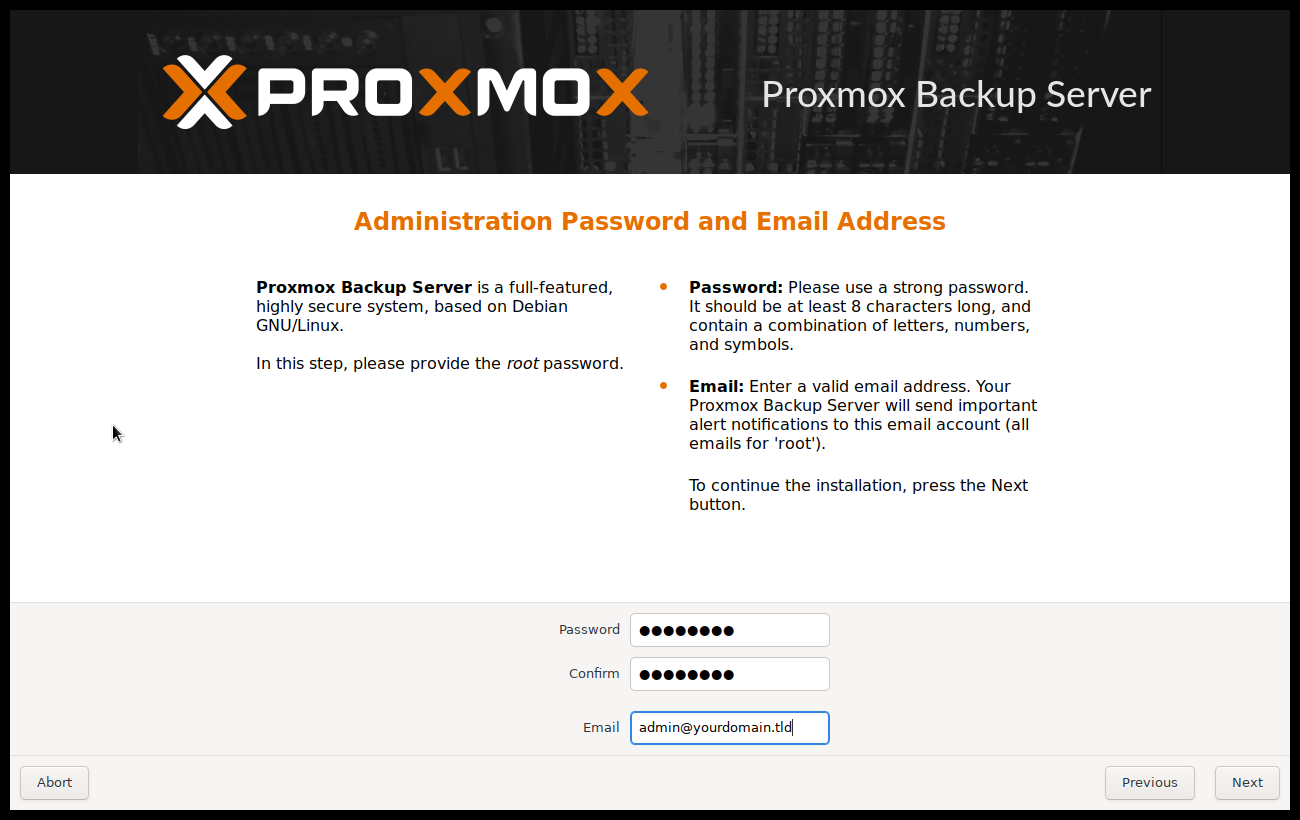
Next the password of the superuser (root) and an email address needs to be
specified. The password must consist of at least 8 characters. It's highly
recommended to use a stronger password. Some guidelines are:
Use a minimum password length of at least 12 characters.
Include lowercase and uppercase alphabetic characters, numbers, and symbols.
Avoid character repetition, keyboard patterns, common dictionary words, letter or number sequences, usernames, relative or pet names, romantic links (current or past), and biographical information (for example ID numbers, ancestors' names or dates).
The email address is used to send notifications to the system administrator. For example:
Information about available package updates.
Error messages from periodic cron jobs.
All those notification mails will be sent to the specified email address.
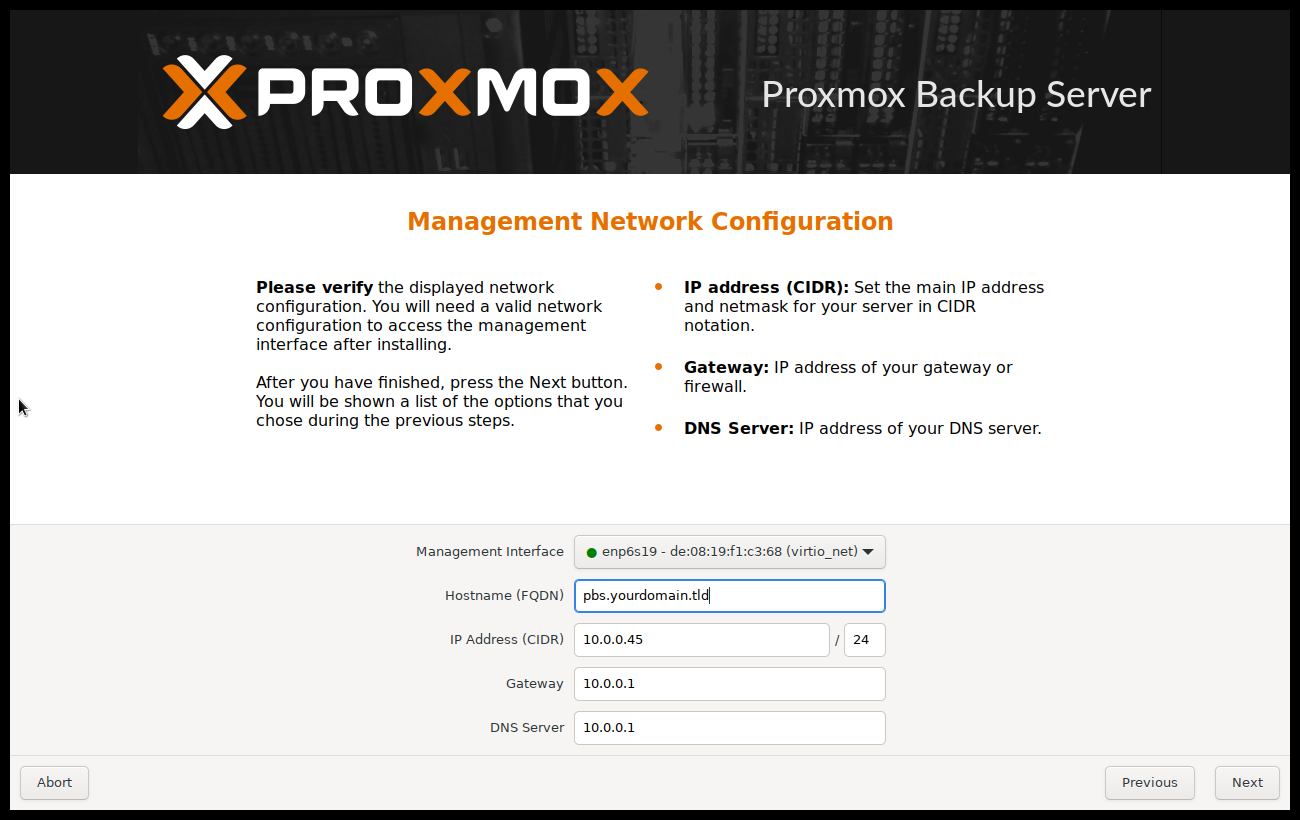
The last step is the network configuration. Network interfaces that are UP show a filled circle in front of their name in the drop down menu. Please note that during installation you can either specify an IPv4 or IPv6 address, but not both. To configure a dual stack node, add additional IP addresses after the installation.

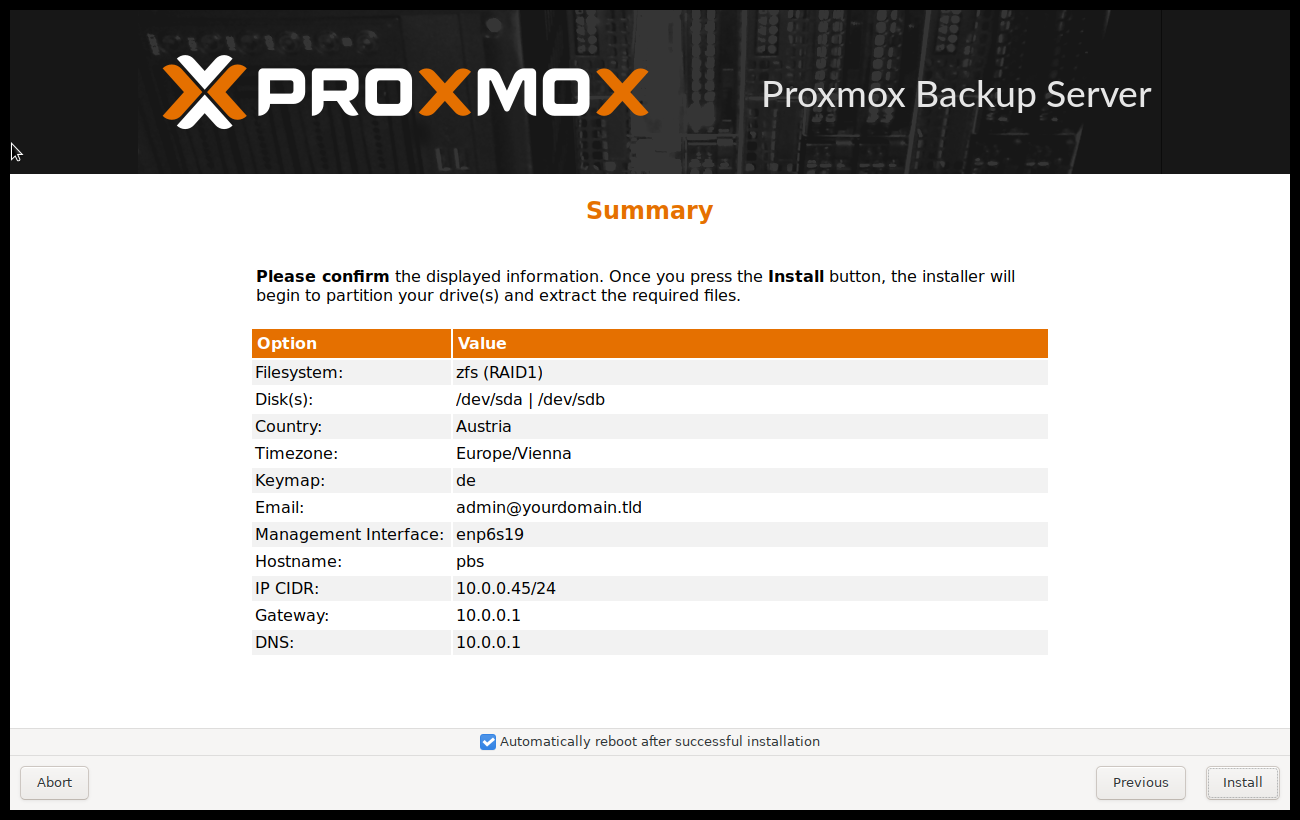
The next step shows a summary of the previously selected options. Please re-check every setting and use the Previous button if a setting needs to be changed.
After clicking Install, the installer will begin to format the disks and copy packages to the target disk(s). Please wait until this step has finished; then remove the installation medium and restart your system.
Copying the packages usually takes several minutes, mostly depending on the speed of the installation medium and the target disk performance.
When copying and setting up the packages has finished, you can reboot the server. This will be done automatically after a few seconds by default.
Installation Failure¶
If the installation failed, check out specific errors on the second TTY
(CTRL + ALT + F2) and ensure that the systems meets the
minimum requirements.
If the installation is still not working, look at the how to get help chapter.
Accessing the Management Interface Post-Installation¶
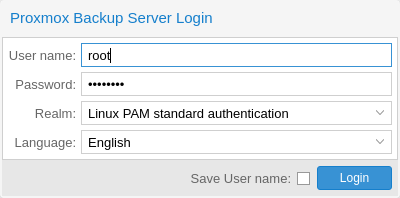
After a successful installation and reboot of the system you can use the Proxmox Backup Server web interface for further configuration.
Point your browser to the IP address given during the installation and port 8007, for example: https://pbs.yourdomain.tld:8007
Log in using the
root(realm Linux PAM standard authentication) username and the password chosen during installation.Upload your subscription key to gain access to the Enterprise repository. Otherwise, you will need to set up one of the public, less tested package repositories to get updates for security fixes, bug fixes, and new features.
Check the IP configuration and hostname.
Check the timezone.
Advanced LVM Configuration Options¶
The installer creates a Volume Group (VG) called pbs, and additional Logical
Volumes (LVs) called root and swap, if ext4 or xfs as filesystem
is used. To control the size of these volumes use:
hdsize
Defines the total hard disk size to be used. This way you can reserve free space on the hard disk for further partitioning.
swapsize
Defines the size of the
swapvolume. The default is the size of the installed memory, minimum 4 GB and maximum 8 GB. The resulting value cannot be greater thanhdsize/8.If set to
0, noswapvolume will be created.minfree
Defines the amount of free space that should be left in the LVM volume group
pbs. With more than 128GB storage available, the default is 16GB, otherwisehdsize/8will be used.
Advanced ZFS Configuration Options¶
The installer creates the ZFS pool rpool, if ZFS is used. No swap space is
created but you can reserve some unpartitioned space on the install disks for
swap. You can also create a swap zvol after the installation, although this can
lead to problems (see ZFS swap notes).
ashift
Defines the ashift value for the created pool. The ashift needs to be set at least to the sector-size of the underlying disks (2 to the power of ashift is the sector-size), or any disk which might be put in the pool (for example the replacement of a defective disk).
compress
Defines whether compression is enabled for
rpool.checksum
Defines which checksumming algorithm should be used for
rpool.copies
Defines the copies parameter for
rpool. Check thezfs(8)manpage for the semantics, and why this does not replace redundancy on disk-level.hdsize
Defines the total hard disk size to be used. This is useful to save free space on the hard disk(s) for further partitioning (for example, to create a swap partition). hdsize is only honored for bootable disks, that is only the first disk or mirror for RAID0, RAID1 or RAID10, and all disks in RAID-Z[123].
ZFS Performance Tips¶
ZFS works best with a lot of memory. If you intend to use ZFS make sure to have enough RAM available for it. A good calculation is 4GB plus 1GB RAM for each TB of raw disk space.
ZFS can use a dedicated drive as write cache, called the ZFS Intent Log (ZIL). Use a fast drive (SSD) for it. It can be added after installation with the following command:
# zpool add <pool-name> log </dev/path_to_fast_ssd>
Adding the nomodeset Kernel Parameter¶
Problems may arise on very old or very new hardware due to graphics drivers. If
the installation hangs during boot, you can try adding the nomodeset
parameter. This prevents the Linux kernel from loading any graphics drivers and
forces it to continue using the BIOS/UEFI-provided framebuffer.
On the Proxmox Backup Server bootloader menu, navigate to Install Proxmox
Backup Server (Console) and press e to edit the entry. Using the arrow
keys, navigate to the line starting with linux, move the cursor to the end
of that line and add the parameter nomodeset, separated by a space from the
pre-existing last parameter.
Then press Ctrl-X or F10 to boot the configuration.
Install Proxmox Backup Server Unattended¶
It is possible to install Proxmox Backup Server automatically in an unattended manner. This enables you to fully automate the setup process on bare-metal. Once the installation is complete and the host has booted up, automation tools like Ansible can be used to further configure the installation.
The necessary options for the installer must be provided in an answer file. This file allows the use of filter rules to determine which disks and network cards should be used.
To use the automated installation, it is first necessary to prepare an installation ISO. For more details and information on the unattended installation see our wiki.
Install Proxmox Backup Server on Debian¶
Proxmox ships as a set of Debian packages which can be installed on top of a standard Debian installation. After configuring the Debian Package Repositories, you need to run:
# apt update
# apt install proxmox-backup-server
The above commands keep the current (Debian) kernel and install a minimal set of required packages.
If you want to install the same set of packages as the installer does, please use the following:
# apt update
# apt install proxmox-backup
This will install all required packages, the Proxmox kernel with ZFS support, and a set of common and useful packages.
Caution
Installing Proxmox Backup on top of an existing Debian installation looks easy, but it assumes that the base system and local storage have been set up correctly. In general this is not trivial, especially when LVM or ZFS is used. The network configuration is completely up to you as well.
Note
You can access the web interface of the Proxmox Backup Server with
your web browser, using HTTPS on port 8007. For example at
https://<ip-or-dns-name>:8007
Install Proxmox Backup Server on Proxmox VE¶
After configuring the Debian Package Repositories, you need to run:
# apt update
# apt install proxmox-backup-server
Caution
Installing the backup server directly on the hypervisor is not recommended. It is safer to use a separate physical server to store backups. Should the hypervisor server fail, you can still access the backups.
Note
You can access the web interface of the Proxmox Backup Server with
your web browser, using HTTPS on port 8007. For example at
https://<ip-or-dns-name>:8007
Client Installation¶
Install Proxmox Backup Client on Debian¶
Proxmox ships as a set of Debian packages to be installed on top of a standard Debian installation. After configuring the APT-based Proxmox Backup Client Repository, you need to run:
# apt update
# apt install proxmox-backup-client
Install Statically Linked Proxmox Backup Client¶
Proxmox provides a statically linked build of the Proxmox backup client that should run on any modern x86-64 Linux system.
It is currently available as a Debian package. After configuring the APT-based Proxmox Backup Client Repository, you need to run:
# apt update
# apt install proxmox-backup-client-static
This package conflicts with the proxmox-backup-client package, as both provide the client as an executable in the /usr/bin/proxmox-backup-client path.
You can copy this executable to other, e.g. non-Debian based Linux systems.
For details on using the Proxmox Backup Client, see Backup Client Usage.
Debian Package Repositories¶
All Debian based systems use APT as a package management tool. The lists of
repositories are defined in /etc/apt/sources.list and the .list or
.sources files found in the /etc/apt/sources.d/ directory. Updates can
be installed directly with the apt command-line tool, or via the GUI.
Repository Formats¶
APT repositories can be configured in two distinct formats, the old single
line format and the newer deb822 format. No matter what format you choose,
apt update will fetch the information from all configured sources.
Single Line¶
Single line repositories are defined in .list files list one package
repository per line, with the most preferred source listed first. Empty lines
are ignored and a # character anywhere on a line marks the remainder of
that line as a comment.
deb822 Style¶
The newer deb822 multiline format is used in .sources files. Each
repository consists of a stanza with multiple key value pairs. A stanza is
simply a group of lines. One file can contain multiple stanzas by separating
them with a blank line. You can still use # to comment out lines.
Note
Modernizing your repositories is recommended under Debian Trixie, as
apt will complain about older repository definitions otherwise. You can
run the command apt modernize-sources to modernize your existing
repositories automatically.
Debian Base Repositories¶
You will need a Debian base repository as a minimum to get updates for all packages provided by Debian itself:
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/debian.sources¶Types: deb
URIs: http://deb.debian.org/debian/
Suites: trixie trixie-updates
Components: main contrib non-free-firmware
Signed-By: /usr/share/keyrings/debian-archive-keyring.gpg
Types: deb
URIs: http://security.debian.org/debian-security/
Suites: trixie-security
Components: main contrib non-free-firmware
Signed-By: /usr/share/keyrings/debian-archive-keyring.gpg
In addition, you need a package repository from Proxmox to get Proxmox Backup updates.
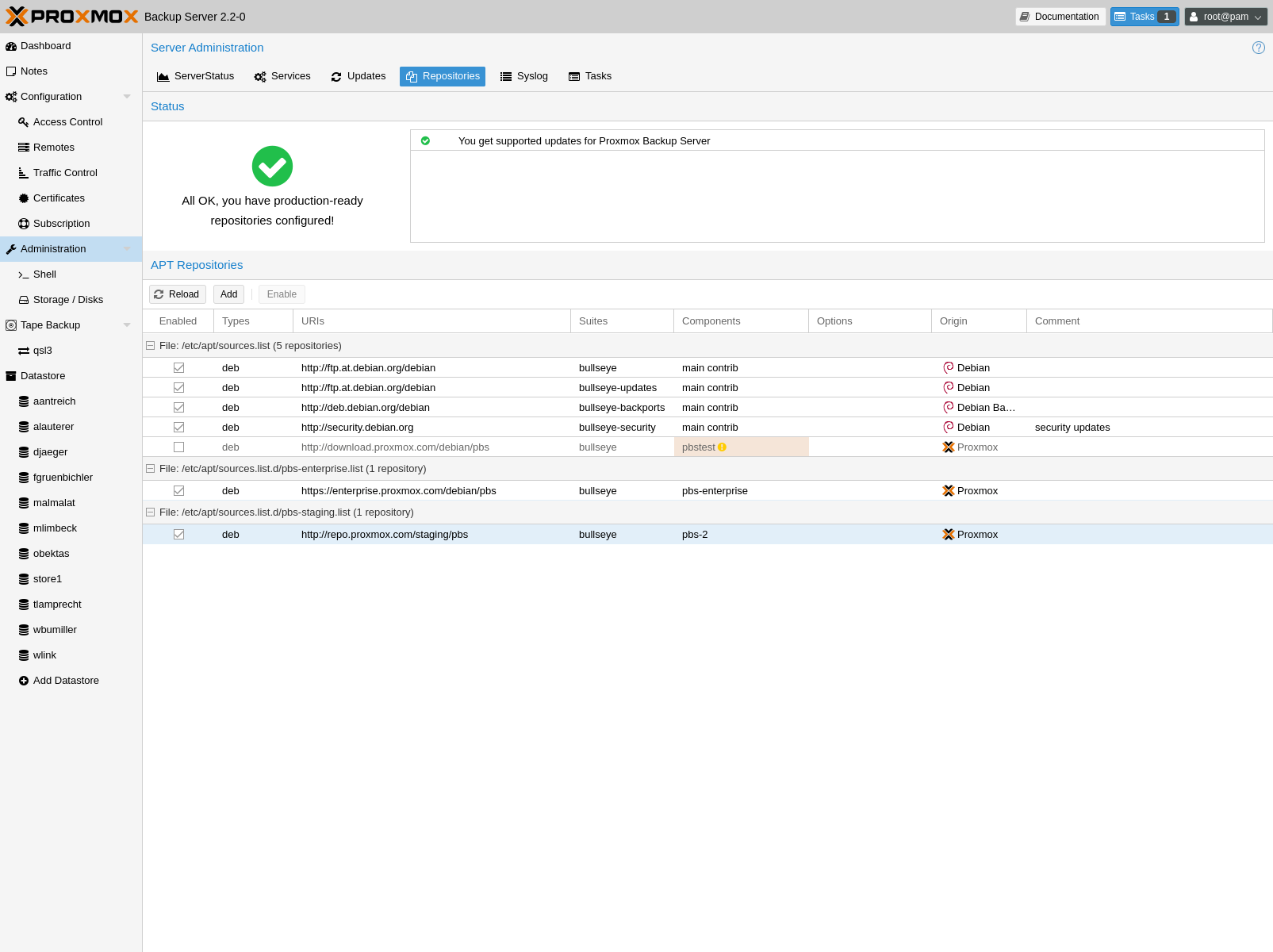
Proxmox Backup Enterprise Repository¶
This is the stable, recommended repository. It is available for
all Proxmox Backup subscription users. It contains the most stable packages,
and is suitable for production use. The pbs-enterprise repository is
enabled by default:
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/pbs-enterprise.sources¶Types: deb
URIs: https://enterprise.proxmox.com/debian/pbs
Suites: trixie
Components: pbs-enterprise
Signed-By: /usr/share/keyrings/proxmox-archive-keyring.gpg
To never miss important security fixes, the superuser (root@pam user) is
notified via email about new packages as soon as they are available. The
change-log and details of each package can be viewed in the GUI (if available).
Please note that you need a valid subscription key to access this repository. More information regarding subscription levels and pricing can be found at https://www.proxmox.com/en/proxmox-backup-server/pricing
Note
You can disable this repository by adding the line Enabled: false
to the stanza.
Proxmox Backup No-Subscription Repository¶
As the name suggests, you do not need a subscription key to access this repository. It can be used for testing and non-production use. It is not recommended to use it on production servers, because these packages are not always heavily tested and validated.
We recommend to configure this repository in
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/proxmox.sources.
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/proxmox.sources¶Types: deb
URIs: http://download.proxmox.com/debian/pbs
Suites: trixie
Components: pbs-no-subscription
Signed-By: /usr/share/keyrings/proxmox-archive-keyring.gpg
Proxmox Backup Test Repository¶
This repository contains the latest packages and is heavily used by developers to test new features.
You can access this repository by adding the following stanza to
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/proxmox.sources:
pbstest¶Types: deb
URIs: http://download.proxmox.com/debian/pbs
Suites: trixie
Components: pbs-test
Signed-By: /usr/share/keyrings/proxmox-archive-keyring.gpg
Proxmox Backup Client-only Repository¶
If you want to use the Proxmox Backup Client on systems using a Linux distribution not based on Proxmox projects, you can use the client-only repository.
Currently there's only a client-repository for APT based systems.
APT-based Proxmox Backup Client Repository¶
For modern Linux distributions using apt as package manager, like all Debian and Ubuntu Derivative do, you may be able to use the APT-based repository.
In order to configure this repository you need to first setup the Proxmox release key. After that, add the repository URL to the APT sources lists.
Repositories for Debian 13 (Trixie) based releases
This repository is tested with:
Debian Trixie
Edit the file /etc/apt/sources.list.d/pbs-client.sources and add the following
snippet
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/pbs¶Types: deb
URIs: http://download.proxmox.com/debian/pbs-client
Suites: trixie
Components: main
Signed-By: /usr/share/keyrings/proxmox-archive-keyring.gpg
Repositories for Debian 12 (Bookworm) based releases
This repository is tested with:
Debian Bookworm
Edit the file /etc/apt/sources.list.d/pbs-client.list and add the following
snippet
/etc/apt/sources.list¶deb http://download.proxmox.com/debian/pbs-client bookworm main
Repositories for Debian 11 (Bullseye) based releases
This repository is tested with:
Debian Bullseye
Edit the file /etc/apt/sources.list.d/pbs-client.list and add the following
snippet
/etc/apt/sources.list¶deb http://download.proxmox.com/debian/pbs-client bullseye main
Repositories for Debian 10 (Buster) based releases
This repository is tested with:
Debian Buster
Ubuntu 20.04 LTS
It may work with older, and should work with more recent released versions.
Edit the file /etc/apt/sources.list.d/pbs-client.list and add the following
snippet
/etc/apt/sources.list¶deb http://download.proxmox.com/debian/pbs-client buster main
SecureApt¶
The Release files in the repositories are signed with GnuPG. APT is using these signatures to verify that all packages are from a trusted source.
If you install Proxmox Backup Server from an official ISO image, the verification key is already installed.
If you install Proxmox Backup Server on top of Debian, download and install the key with the following commands:
# wget https://enterprise.proxmox.com/debian/proxmox-archive-keyring-trixie.gpg -O /usr/share/keyrings/proxmox-archive-keyring.gpg
Note
The wget command above adds the keyring for Proxmox releases based on Debian Trixie. Once the proxmox-archive-keyring package is installed, it will manage this file. At that point, the hashes below may no longer match the hashes of this file, as keys for new Proxmox releases get added or removed. This is intended, apt will ensure that only trusted keys are being used. Modifying this file is discouraged once `proxmox-archive-keyring` is installed.
Verify the SHA256 checksum afterwards with the expected output below:
# sha256sum /usr/share/keyrings/proxmox-archive-keyring.gpg
136673be77aba35dcce385b28737689ad64fd785a797e57897589aed08db6e45 /usr/share/keyrings/proxmox-archive-keyring.gpg
and the md5sum, with the expected output below:
# md5sum /usr/share/keyrings/proxmox-archive-keyring.gpg
77c8b1166d15ce8350102ab1bca2fcbf /usr/share/keyrings/proxmox-archive-keyring.gpg
Note
Make sure that the path that you download the key to, matches the
path specified in the Signed-By: lines in your repository stanzas from
above.
Repository Access Behind HTTP Proxy¶
Some setups have restricted access to the internet, sometimes only through a central proxy. You can setup a HTTP proxy through the Proxmox Backup Server's web-interface in the Configuration -> Authentication tab.
Once configured this proxy will be used for apt network requests and for checking a Proxmox Backup Server support subscription.
Standard HTTP proxy configurations are accepted, [http://]<host>[:port] where the <host> part may include an authorization, for example: http://user:pass@proxy.example.org:12345